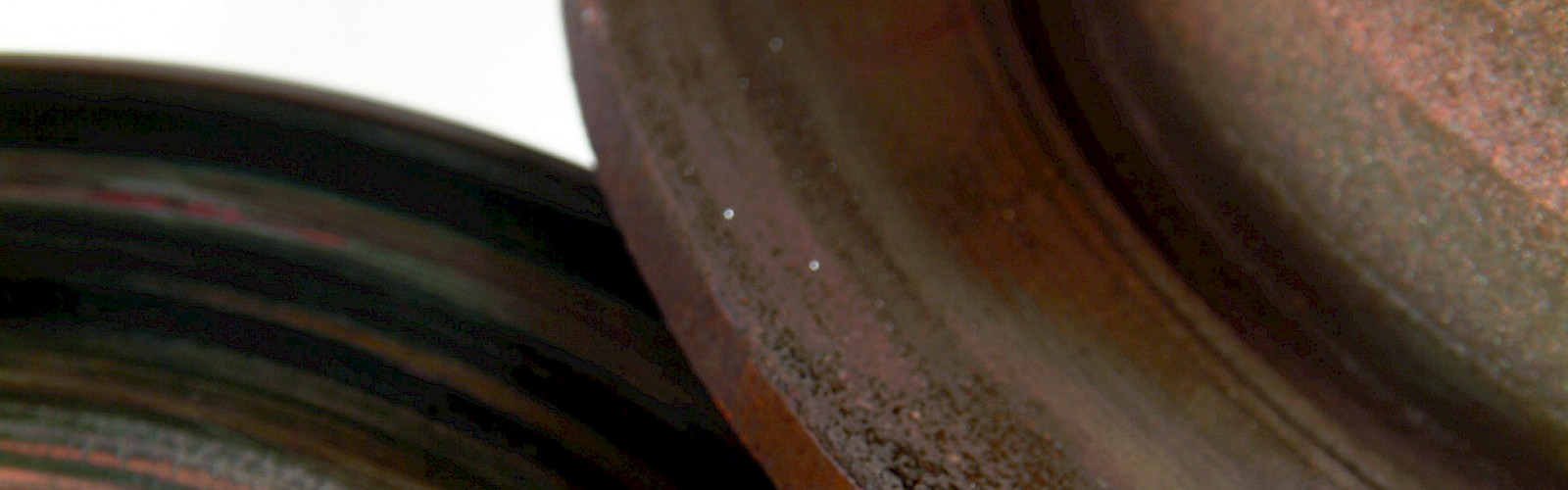
Here you will find a list of the most common damage patterns of brake discs in order to enable an easier assessment and processing of complaints
If you would like to receive the damage pictures as a poster, we will be happy to send it to you: Request damage poster.
-
 Contaminated contact surface
Contaminated contact surface
-
 Pressure marks and corrosion
Pressure marks and corrosion
-
 Torque and tightening sequence
Torque and tightening sequence
-
 Hub run-out
Hub run-out
-
 Running-in phase
Running-in phase
-
 Intensive use
Intensive use
-
 Wear limit
Wear limit
-
 Thermal Overload
Thermal Overload
-
 Periods of non-use
Periods of non-use
-
 Mal function of parking brake
Mal function of parking brake
-
 Glazed brake pads / friction surface
Glazed brake pads / friction surface
-
 Position of caliper / pad surface
Position of caliper / pad surface
-
 Uneven wear of braking surface
Uneven wear of braking surface
-
Contaminated contact surface
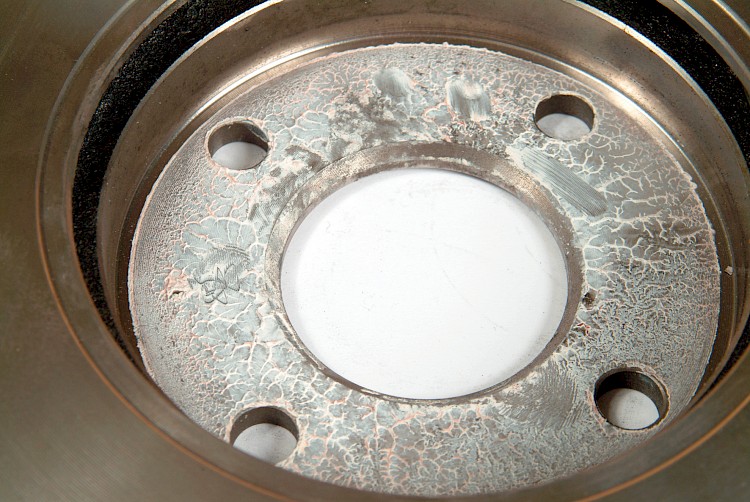

- Symptom:
-
- Contact surface is contaminated / smeared with grease and / or paste
- Cause:
-
- Failure to observe recommendations in ZIMMERMANN mounting instructions
- Brake discs / brake drums should be assembled dry, cleanly, and metallically bright
- Effect:
-
- Grease / paste bind foreign particles which get trapped between disc / drum and hub
- Coplanar assembly not possible or only possible to a limited degree
- Brake disc / brake drum is assembled "lopsidedly" and runs increasingly untrue with increased mileage
- Axial run-out caused by assembly can be checked on the vehicle itself, without the need for a test drive, by using a dial gauge / micrometer gauge and magnetic stand!
- Steering wheel wobble / judder after approx. 1,500 – 5,000 km
-
Pressure marks and corrosion
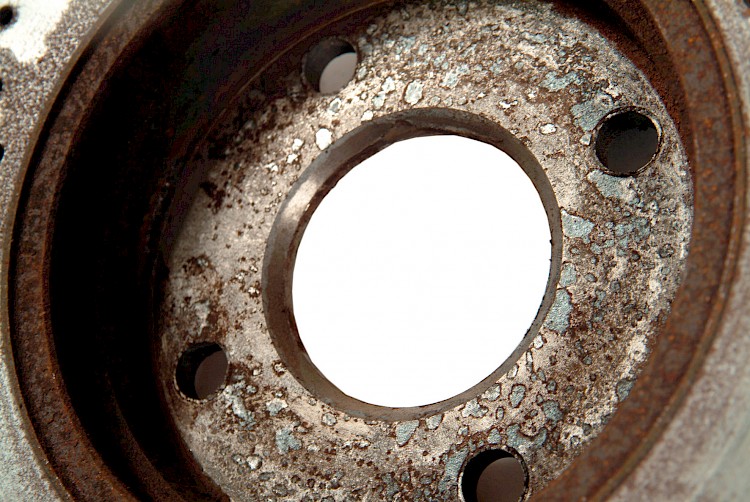

- Symptom:
-
Contact surface shows pressure marks and is corroded in parts
- Cause:
-
- Contact surface of wheel hub has not been cleaned at all or only insufficiently
- Failure to observe recommendations in ZIMMERMANN mounting instructions
- Brake discs / brake drums should be assembled dry, cleanly, and metallically bright
- Effect:
-
- Dirt and / or rust particles have become trapped between brake disc / brake drum and hub
- Coplanar assembly not possible or only possible to a limited degree
- Brake disc / brake drum is assembled "lopsidedly” and runs increasingly untrue with increased mileage
- Axial run-out caused by assembly can be checked on the vehicle itself, without the need for a test drive, by using a dial gauge / micrometer gauge and magnetic stand!
- Steering wheel wobble / judder after approx. 1,500 – 5,000 km
-
Torque and tightening sequence
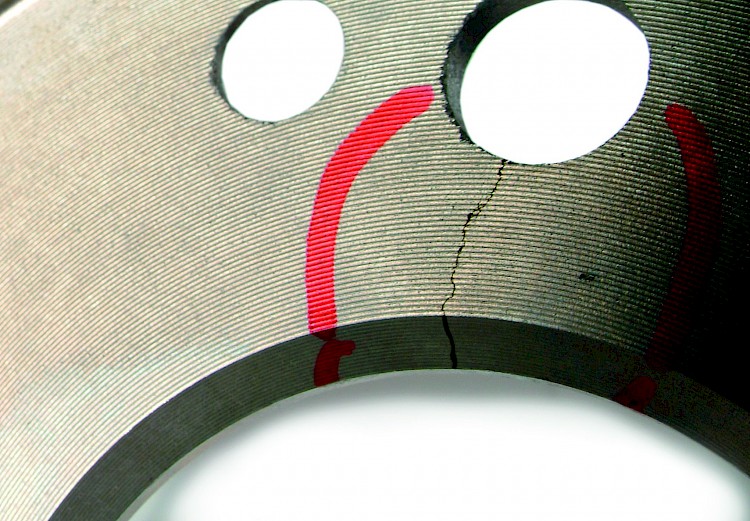

- Symptom:
-
- The contact surface is cracked in the vicinity of the hole(s)
- The contact surface is cracked in the vicinity of the hole(s)
- Cause:
-
- The wheel bolts / wheel nuts have been tightened with excessive torque and / or in the incorrect order
- Failure to observe vehicle manufacturer’s instructions
- Failure to observe recommendations in ZIMMERMANN mounting instructions
- Effect:
-
- Coplanar assembly not possible or only possible to a limited degree
- Brake disc / brake drum is assembled "lopsidedly” and runs untrue immediately after assembly
- Axial run-out caused by assembly can be checked on the vehicle itself, without the need for a test drive, by using a dial gauge / micrometer gauge and magnetic stand!
- Deformation of contact surface (even if no cracks are visible!)
-
Hub run-out
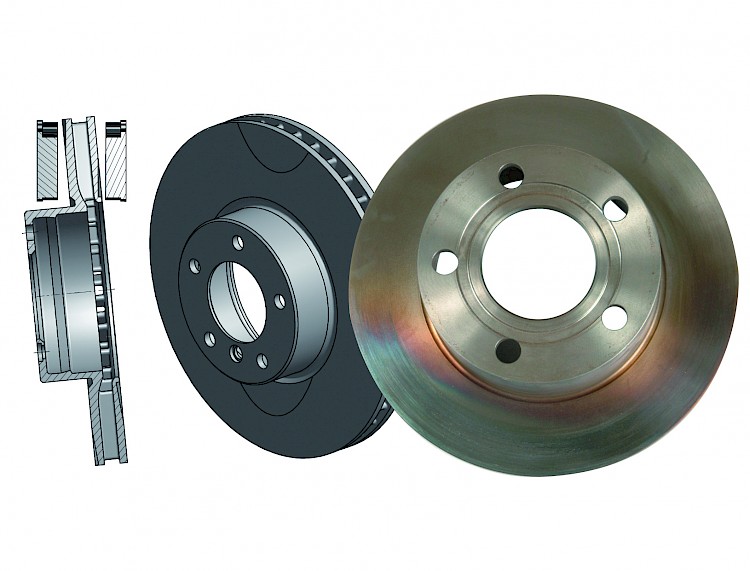

- Symptom:
-
- Asymmetrical wear of brake friction faces
- Blue-black hot spots
- Cause:
-
- Functional axes of brake disc and caliper are out of alignment
- Wheel hub is mounted off straight in relation to the caliper
- Axial run-out caused by assembly can be checked on the vehicle itself, without the need for a test drive, by using a dial gauge / micrometer gauge and magnetic stand!
- Effect:
-
- Brake pedal vibration / judder
- Steering wheel wobble
- Brake fade
- Wear limit reached prematurely
- Partial thermal overload due to constant grinding of friction ring on pad
-
Running-in phase
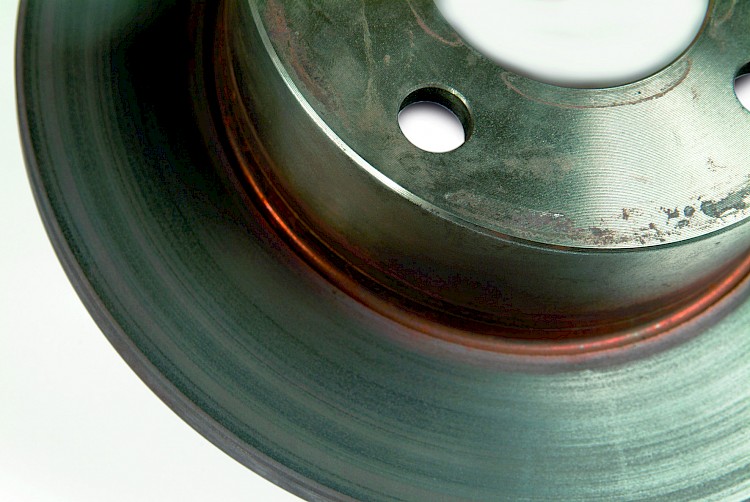

- Symptom:
-
- Friction surface and / or hub showing the so-called annealing colors (off-white to grey)
- Cause:
-
- Running-in phase too short
- Violent braking / panic stops carried out during running-in phase
- Use of incorrect pads (friction coefficient, composition, quality)
- Effect:
-
- Brake pedal vibration
- Steering wheel wobble
- Brake fade
- Due to thermal overload
- Brake disc anneals, there can be structural transformations, alteration of the mechanical properties of the cast material
-
Intensive use
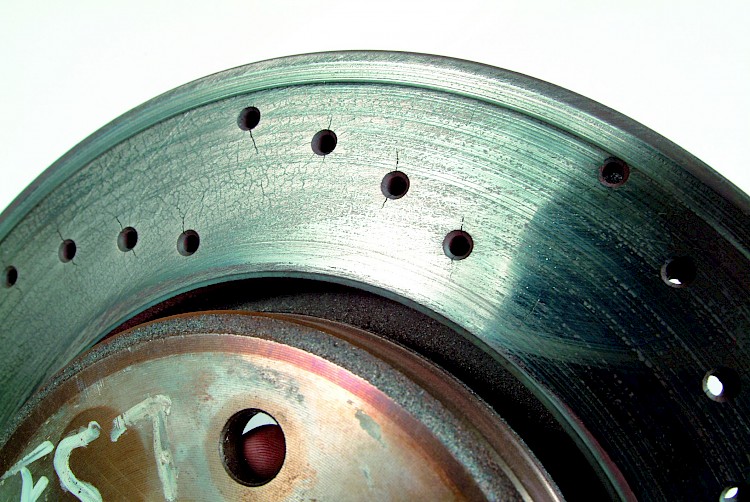

- Symptom:
-
- The brake friction faces are showing blue-black so-called hot spots.
- Net-like hairline cracks have developed into larger radial heat cracks mainly in the centre of the friction ring.
- Cause:
-
- Running-in phase too short
- Violent braking / panic stops carried out during running-in phase
- Use of incorrect pads (friction factor, composition, quality)
- Individual vehicle handling
- Effect:
-
- Brake pedal vibration
- Steering wheel wobble
- Brake fade
- Due to thermal and / or mechanical overload: the brake disc anneals and / or there is structural transformation, alteration of the mechanical properties of the cast material and / or friction surface / brake friction faces can crack through
-
Wear limit
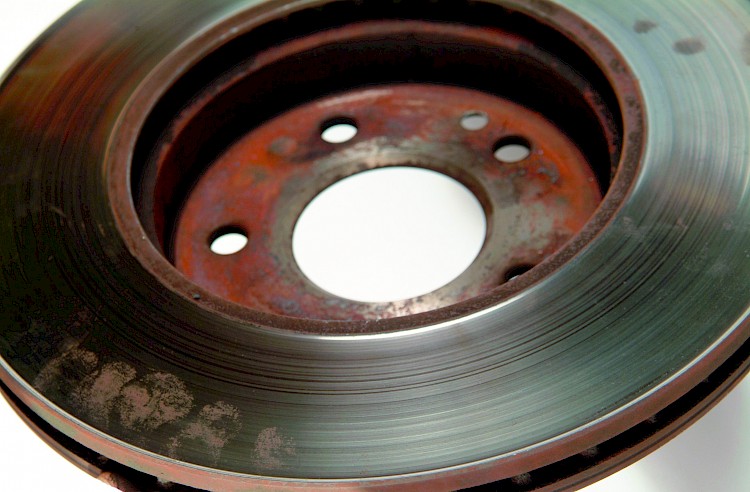

- Symptom:
-
The brake friction faces are unduly worn; there is a clear difference in thickness between
the contact area of the pads and the original thickness of the friction surface - Cause:
-
- There is a substantial shortfall below the prescribed wear limit
- Failure to observe recommendations in ZIMMERMANN mounting instructions
- Wear limit is stamped into the ouside diameter of the brake surface or onto the hub
- Effect:
-
- Steering wheel wobble
- Brake fade: "long" brake pedal travel
- Due to thermal and / or mechanical overload: the brake disc anneals and / or there is structural transformation, alteration of the mechanical properties of the cast material and / or friction ring can break away from the hub
-
Thermal Overload
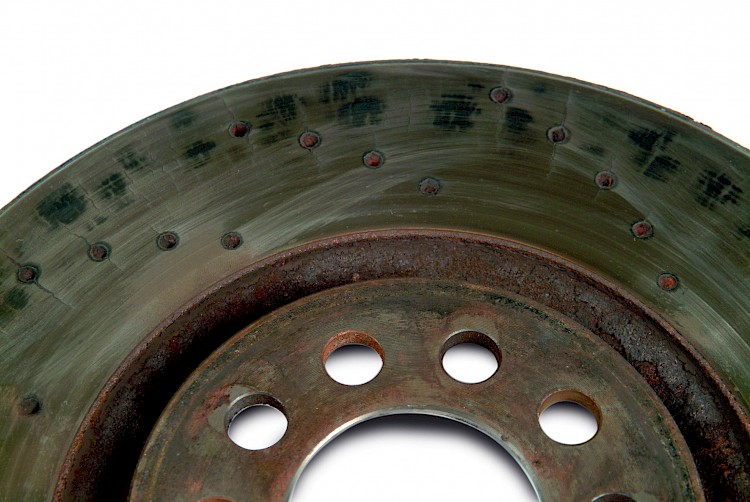

- Symptom:
-
- The brake friction faces are showing blue-black so-called hot spots
- Net-like hairline cracks have developed into larger radial heat cracks
- Cause:
-
- Thermal overload
- Individual vehicle handling
- Effect:
-
- Brake pedal vibration
- Steering wheel wobble
- Brake fade
- Noise generation (humming, droning, grating)
- Due to thermal and / or mechanical overload: the brake disc anneals and / or there is structural transformation, alteration of the mechanical properties of the cast material and / or friction surface / brake friction faces can crack through
-
Periods of non-use
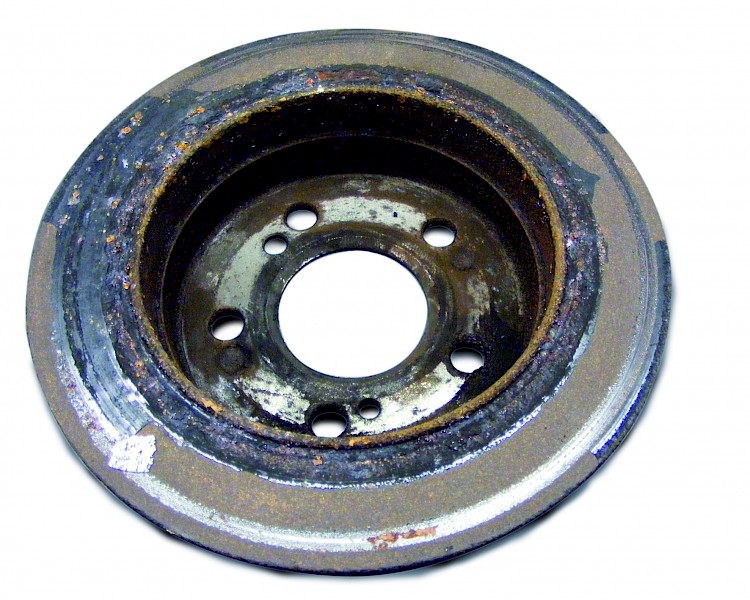

- Symptom:
-
- On the braking area there are layers of corrosion, some of them thick, peeling off the friction ring.
- Cause:
-
- The vehicle concerned was not in use for a relatively long period (garaged vehicle / stored vehicle)
- The vehicle concerned was not used for relatively long periods after being driven in damp / wet conditions (water damage)
- Effect:
-
- Brake pedal vibration / judder
- Steering wheel wobble / shimmy
- Brake fade: Brake pedal becomes "hard"
- Noise generation (humming, droning, grating)
- When started up again the friction ring and pads are badly damaged by the extremely hard scale particles becoming detached
- Fragments of disc and pad material are torn out
-
Mal function of parking brake
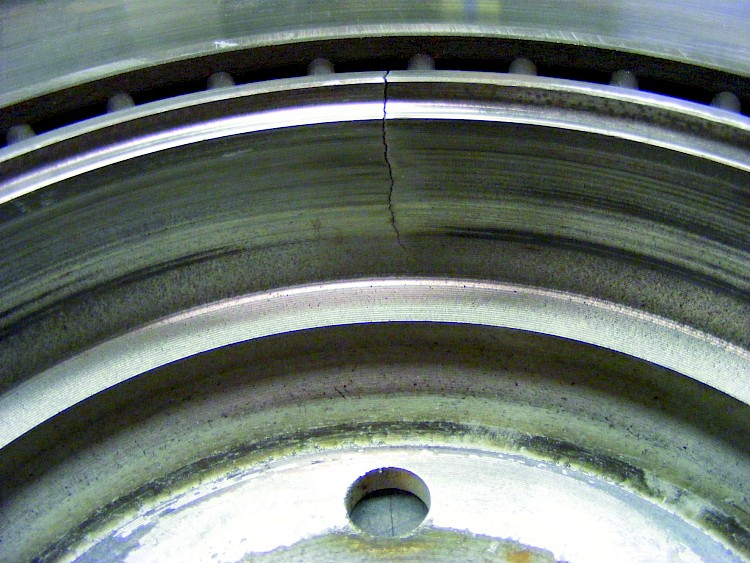

- Symptom:
-
- The brake disc has radial cracks in the area of the parking brake diameter (hand brake), some of which continue across the thermal insulation channel into the braking area
- The parking brake area diameter (hand brake), groove for thermal insulation and braking area are exhibiting the so-called annealing colors
- Cause:
-
- The vehicle was driven with the parking brake on (applied) for a relatively long period and then also stopped with the parking brake applied
- The mechanics of the parking brake and / or the cables are sluggish or not serviceable
- Effect:
-
- Due to thermal and / or mechanical overload:
the brake disc anneals and / or there is structural transformation, alteration of the mechanical properties of the cast material and / or friction surface / brake friction faces and hub can crack through - Acute noise generation (humming, droning, knocking) when braking
- Acute noise generation (grinding, rubbing, rattling) when applying the parking brake
- Due to thermal and / or mechanical overload:
-
Glazed brake pads / friction surface
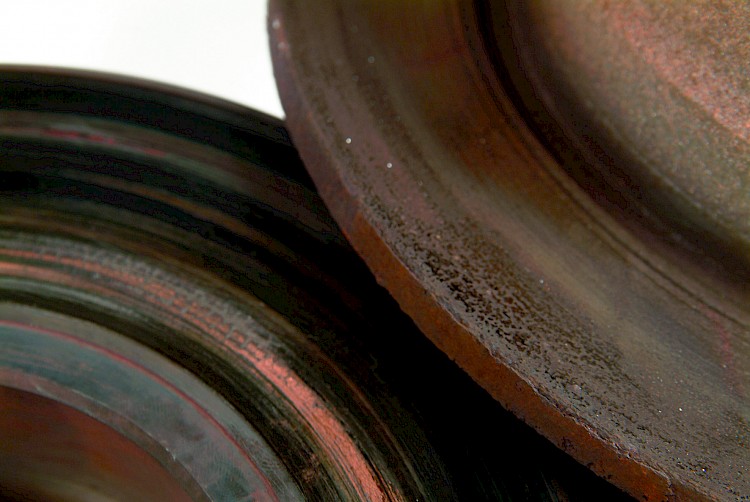

- Symptom:
-
- Particles of the friction material have worked / „burnt“ into the braking area
- Shiny surface on brake friction faces
- Cause:
-
- Inferior pad quality
- Consistency of binding agent, lubricant and filler
- Non-homogeneity of friction material (uneven distribution of abrading medium)
- Sudden quenching of hot brake disc
- Flaking of particles from the friction ring
- Occurs frequently with relatively new brake discs which are still insufficiently run in
- Inferior pad quality
- Effect:
-
- Brake fade: Brake pedal becomes „hard”
- Excessive wear of brake disc and pad
- Noise generation (humming, droning, grating)
-
Position of caliper / pad surface
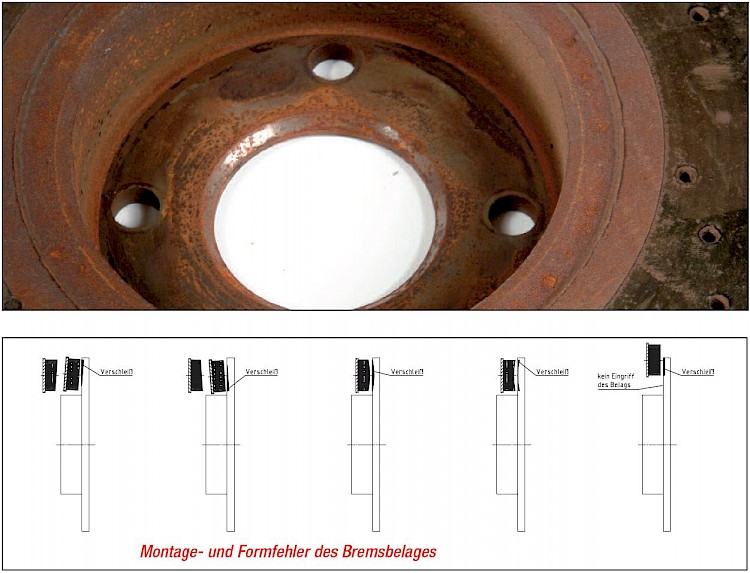
- Symptom:
-
- The brake friction faces are showing signs of uneven pad contact, not reaching across the entire width of the friction ring
- Some corroded areas on the brake friction faces
- Pads not making contact in this area
- The brake friction faces are showing signs of uneven pad contact, not reaching across the entire width of the friction ring
- Cause:
-
- Inferior pad quality
- Evenness / plane parallelism not guaranteed
- Functional axes of brake disc and caliper are out of alignment
- Caliper is mounted off straight in relation to the brake disc / wheel hub
- Partial loss of friction material
- Inferior pad quality
- Effect:
-
- Brake fade
- Brake pedal becomes "hard"
- Reduction of friction surface actually available
- Partial excessive wear of brake disc and pad
- Thermal and / or mechanical overload
- Steering wheel wobble / shimmy
- Brake fade
-
Uneven wear of braking surface
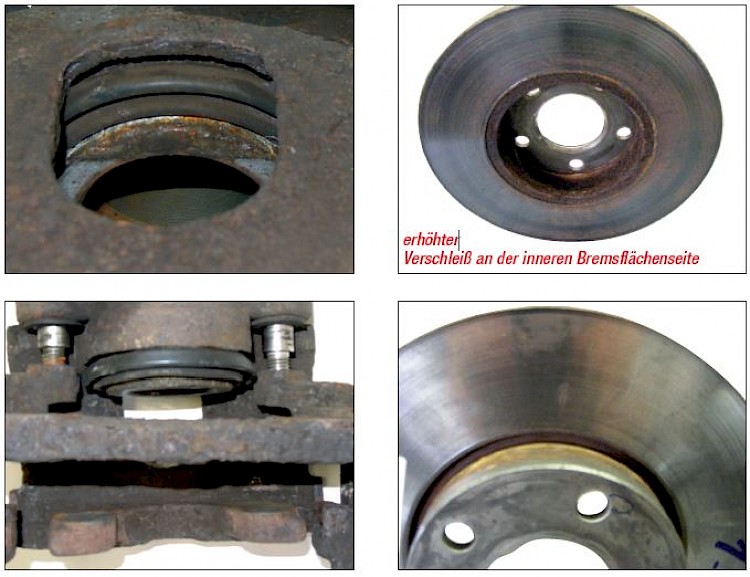

- Symptom:
-
- Whisteling and squeaking not only while braking
- Cause:
-
- Components of the brake caliper inter alia, piston, sealing elements, pins are not checked for wear and / or damage as recommended in the manual
- Piston and guide pins are sluggisch or operate uneven; piston cannot be resetted completely
- Effect:
-
- Less braking effect
- Uneven and increased wear
- Uneven thermal overload of the brake disc because of bad sliding of pins
- Uneven pressure on the braking surface may lead to a demolished hub because of axial force

